Medically reviewed by Dr. Ramesh Gaddam, M.D. — Written by Sumalatha, D.N.H.E
Isolated Diastolic Hypertension (IDH) is when the lower number in your blood pressure reading is consistently high, while the top number stays normal.
When your heart beats, it creates pressure on your artery walls. This is called systolic pressure.
The bottom number, diastolic pressure, shows the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
Keeping your blood pressure in check is important for staying healthy. High blood pressure, whether it’s just the bottom number or both, can lead to serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, and kidney issues.
It’s crucial to manage your blood pressure to lower these risks.
Blood Pressure Readings
There are two types of Blood Pressure Readings:
- Systolic Pressure: This is the top number and measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats.
- Diastolic Pressure: This is the bottom number and measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
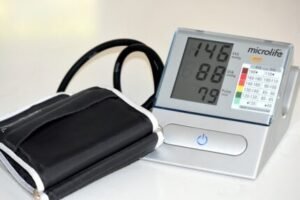
Normal Blood Pressure Range
A normal blood pressure reading is around 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
This means your systolic pressure is 120 mm Hg, and your diastolic pressure is 80 mm Hg.
Hypertension
Hypertension is a term for high blood pressure.
There are different types of hypertension, and one of them is Isolated Diastolic Hypertension (IDH).
This happens when only your diastolic pressure is high, but your systolic pressure is normal.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to this condition, both primary and secondary.

(i) Primary Causes
Age-related Changes in Blood Vessels:
As we get older, our blood vessels become less flexible, which can lead to increased diastolic pressure.
Genetics and Family History:
Your genes play a role in how your blood pressure behaves.
If high blood pressure runs in your family, you might be at higher risk for IDH.
Lifestyle Factors:
Certain lifestyle choices can contribute to IDH, including an unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, and high levels of stress.
These factors can strain your cardiovascular system, leading to elevated diastolic pressure.
(ii) Secondary Causes
Kidney Disease:
Problems with your kidneys can affect their ability to regulate blood pressure, leading to IDH.
Endocrine Disorders:
Medications:
Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids, can cause a rise in blood pressure, particularly diastolic pressure.
Signs and Symptoms
Isolated Diastolic Hypertension (IDH) often doesn’t cause noticeable symptoms until complications develop.
Being alert to warning signs is crucial, particularly during complications.

Typically Asymptomatic until Complications Arise
In many cases, IDH doesn’t present obvious symptoms until it leads to complications.
This means you might not feel anything unusual even if your diastolic pressure is elevated.
Possible Symptoms of Complications
While IDH itself may not cause symptoms, complications arising from sustained high diastolic pressure can manifest with certain signs, including:
Headache:
Persistent headaches, especially in the back of the head, can indicate increased pressure within the blood vessels.
Vision Changes:
Blurred vision, double vision, or other vision problems can occur due to increased pressure on the blood vessels supplying the eyes.
Diagnosis
IDH is diagnosed by regularly checking blood pressure.

Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is crucial in identifying this condition.
Regular blood pressure monitoring is important to detect abnormalities, including IDH.
Diagnosing IDH is based on consistent readings showing elevated diastolic pressure while systolic pressure remains within normal ranges.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM)
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) is a method used to measure blood pressure over 24 hours, providing a more comprehensive assessment of blood pressure variations.
Benefits of ABPM
ABPM reduces the likelihood of white-coat hypertension.
It also detects nocturnal hypertension, which may not be evident with standard clinic measurements.
ABPM provides a detailed profile of blood pressure patterns over an extended period.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring helps diagnose and treat isolated diastolic hypertension better.
Isolated Diastolic Hypertension (IDH) poses significant risks for various complications, including cardiovascular diseases and target organ damage.
Complications
Complications related to Isolated Diastolic Hypertension (IDH) are as follows:
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction):
Did you know that having high diastolic pressure can put a lot of strain on your heart?
If it’s left unchecked, it can even increase your risk of developing coronary artery disease, which can ultimately lead to heart attacks.
It’s always important to monitor your blood pressure levels and take the necessary steps to keep your heart healthy and happy!
Stroke (Cerebrovascular Accident):
High blood pressure damages the blood vessels supplying the brain, increasing the likelihood of stroke due to reduced blood flow or vessel rupture.
Kidney Damage (Nephropathy):
Retinal Damage:
If not treated, high blood pressure can result in vision problems and even permanent vision loss by harming the blood vessels in the retina.
Treatment Options
1. Lifestyle Modifications

Dietary Changes:
The DASH diet is effective in reducing blood pressure and promoting heart health.
It focuses on eating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing sodium intake.
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can improve cardiovascular health and help lower blood pressure.
Stress Management Techniques:
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can lower stress and blood pressure.
Limiting Alcohol Intake and Quitting Smoking:
Alcohol and smoking raise blood pressure. Limiting alcohol and quitting smoking improves control.
2. Medication Options

Diuretics:
Diuretics help the body eliminate excess sodium and water, reducing blood volume and lowering blood pressure.
ACE Inhibitors:
Blood vessels are relaxed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which enable blood to flow more smoothly and reduce blood pressure.
Calcium Channel Blockers:
These medications prevent calcium entry into the heart and blood vessels, which relaxes the arteries and lowers blood pressure.
Beta-Blockers:
Beta-blockers lower heart rate and blood pressure by reducing heart workload.
Eating a heart-healthy diet like DASH and limiting alcohol and quitting smoking can help lower blood pressure.
Prevention
Taking Proactive Steps to Prevent Isolated Diastolic Hypertension

To prevent Isolated Diastolic Hypertension (IDH), adopt healthy habits, get regular check-ups, and manage underlying health conditions.
Healthy Diet:
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels and preventing IDH requires a balanced diet that includes fruits, veggies, whole grains, and lean proteins.
It is important to avoid sodium, saturated fats, and processed foods.
Regular Exercise:
Stress Management:
Limiting Alcohol and Quitting Smoking:
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and quitting smoking are essential steps in preventing hypertension and reducing the risk of IDH.
Health Check-Ups & BP Monitoring

Annual Health Check-ups:
Blood Pressure Monitoring:
Diabetes Management:
Kidney Disease Management:
Conclusion
Medically reviewed by Dr. Ramesh Gaddam, M.D.

General Physician, Diabetologist, and Critical Care Specialist.
Discover more from Health Build-Up
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Pingback: High Blood Pressure: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment